What Is Inertia Constant of Synchronous Generator
Hence it is necessary to study and control the frequency range for a stable power system. This constant H is also known as inertia constant.

Measuring Grid Inertia Accurately Will Enable More Efficient Frequency Management Watt Logic
Fossil fuel generators burn fossil fuels to produce high temperature and pressure gases steam in steam turbines air in gas.
. We have old 14 MVA fuel generators with mechanic speed governors with 2 s H inertia constants. A synchronous generator operates with high inertia which is valuable to the grid. By definition the inertia constant for a synchronous machine is defined as tex H 12 J omega_02 S tex where tex a H textconstant of inertia s tex tex b S textrated power of synchronous machine MW tex tex c omega_0 textnominal angular frequency rads tex.
My colleagues of the Dispatch Center prefer with low load to use the old fuel generators because of their higher H constants. Consider inertial constant of a machine as Here KE is kinetic energy of a machine in Mega Joules and S is rating of a machine in VA. Power grid inertia from rotating generators has been abundantand.
SCR Short-Circuit Ratio - the ratio of the field. Wind turbines have much less rotational inertia PV solar none. Once each turning gear achieves its maximal rpm for obtaining the maximal inertia torsion and kinetic for the generator to output the power.
The rotating synchronous generator. Moment of Inertia Turbine plus Generator R 2_____ lb-ft 10. Here Here J is rotor moment of inertia in Kg m 2 and ω sm is synchronous speed in rad mechanicals.
You can see that the spinning inertia of a synchronous generator will keep the generated power at a consistent frequency. Synchronous inertia and frequency stability. Inertia Time Constant on machine base.
Globally frequency in each country is either set at 50 Hz or 60 Hz. 2 à 2 Ø MW 3 Where G is the MVA rating of the machine H is the inertia constant. The ratio of the total rotational energy stored in the rotating components divided by the generators nameplate MVA rating.
Wind turbine generators are built to be lightweight with low inertia adding to the need for the inertial properties of synchronous condensers Plan Wisely With wind and solar flooding onto the grid and coal and natural gas power plants retirements being announced on a regular basis there is a desire to decommission these units as. It is important to note that the kinetic energy of the system is an energy dimension parameter usually given in MWs while the synchronous inertia constant is a time dimension usually given in seconds attribute. What happens when the frequency drops.
The inertia constant H. H is a measure of the alternator rotors stored kinetic energy based on the operational running speed and alternator output kVA rating - remember the alternator could well be running at unity power factor so kVA is used rather than kW. Inertia from rotating electrical generators in fossil nuclear and hydroelectric power plants represents a source of stored energy that can be tapped for a few seconds to provide the grid time to respond to power plant or other system failures.
2H Two times the system inertia in MWs MVA f t P 2H H Inertia constant in MWs MVA J Moment of inertia in kgm2 of the rotating mass ω nominal speed of rotation in rads MVA MVA rating of the machine ½Jω2 MVA H MVA Typical H for a synchronous generator can range from 2 to 9 seconds MWsMVA. Inertia constant is the ratio of kinetic energy of a rotor of a synchronous machine to the rating of a machine in MVA. Where w2pirpm60 314 for 3000rpm 157 for 1500rpm and so on J 4WK2.
The Inertia constant H of a generator-turbine unit is defined as the ratio of kinetic energy stored at the synchronous speed ω syn m to the generator kVA or MVA rating SB. Inertia Constant The dynamics of the rotor is defined by the second order swing equation of the synchronous which is a non linear differential equation and is given by- À Á Ù. During the lifetime of a unit exciter or governor equip- Found inside Page 373 generating unit carrying 844 MW of load tripped off by loss of field relay.
Inertia constant H MW-secondsMVA. Components and their rotational speed not the electrical rating of the generator. Any disturbance to the grid must work against all the inertia of the grid - you can think about synchronous generators pushing back against disturbances.
Synchronous inertia and frequency stability Physics World. 𝐻 1 2𝐽𝜔2 MVA. The relationship between M and H can be derived as below.
H is provided as a. As we move away from large power plants with massive rotating turbogenerators there will be problems with maintaining lock-step grid system frequency stability. Inertia Constant - Generator.
When the shaft turns at a constant rotational velocity rotational kenitic energy is stored. Historically in the US. E Jw22 and HEP.
Then we have modern 21 MVA natural gas generators with digital speed governors but with only 134 s H inertia constants. The inertia constant H in s - is the ratio of energy stored in the rotor at nominal speed E in Joules over the nominal power P in W of the machine. Mimicking this can be done by damping the response of the VSG.
Where Ssys is the cumulative apparent power of each generator in the system. _____ sec or MJMVA 11. FREQUENCY Hz System H or inertia constant is a measure of the energy.
The inertia constant of the current GB system was estimated using the low frequency incident that occurred on 27 May 2008. The inertia constant is more a. SYNCHRONOUS GENERATORS CONNECTED TO PGE ELECTRIC SYSTEM TECHNICAL DATA SHEET FOR SYNCHRONOUS MACHINES.
It is a constant related to the rotational inertia of all masses that are mechanically connected to a given generator shaft. The overall system inertia constant will be dropped after replacing a generator by a renewable energy source such as solar and wind power. Rotational inertia is a measure of the kinetic energy present in a generators spinning rotor and system inertia is the total amount of rotational inertia available to the grid from online synchronously-connected generators 10.
Answer 1 of 3. Rotational inertia is a property of the real synchronous generator. Let G Rated MVA capacity of Machine f system frequency As per definition of H H Kinetic Energy G But Kinetic Energy of Machine Mω2 M x 2πf2 Mπf Therefore H Mπf G M GH πf Mega Joule Second Radian.
The grid in Australia is kept at a constant frequency of 50 Hz whereas the grid in the USA is set at 60 Hz.
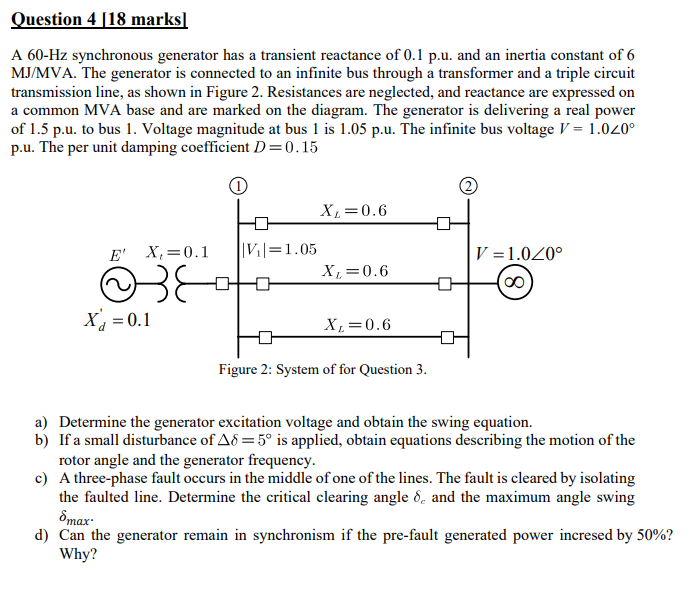
Solved Question 4 18 Marks A 60 Hz Synchronous Generator Chegg Com
What Is The Inertia Constant Of A Synchronous Generator After A Power Generation Loss The Power Output Of The Remaining Generators Goes Up Immediately What Has The Inertia Constant To Do With

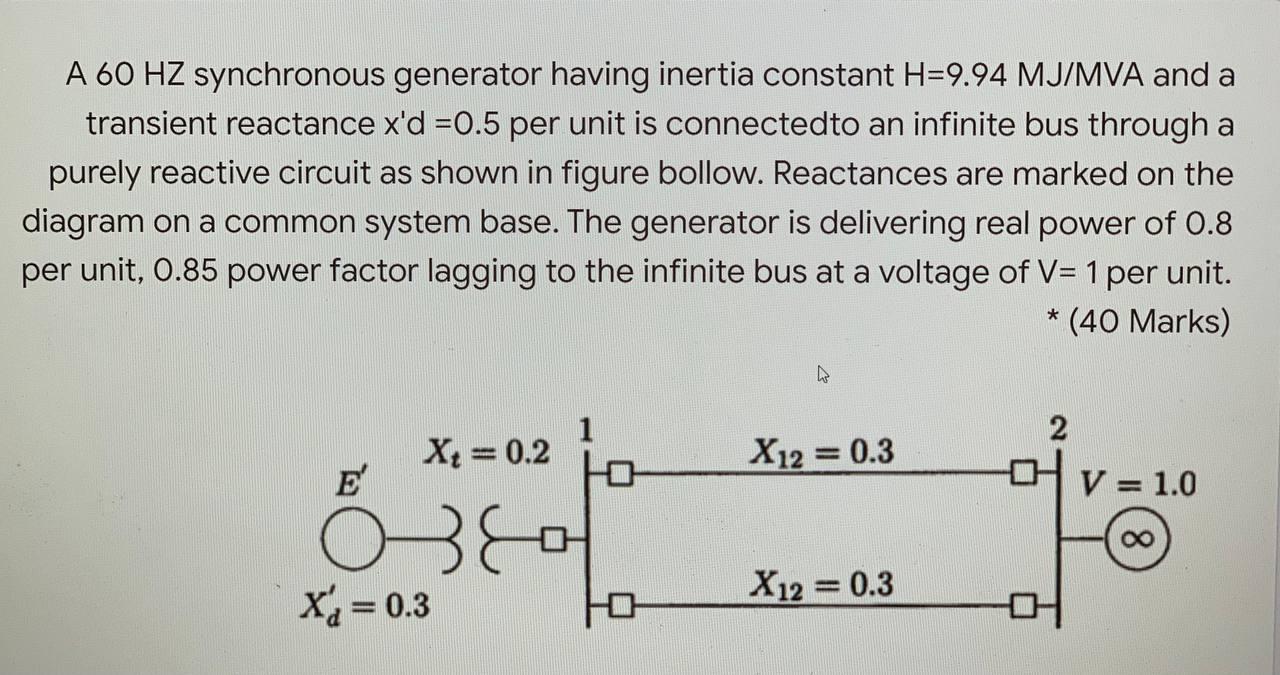
Solved A 60 Hz Synchronous Generator Having Inertia Constant Chegg Com
No comments for "What Is Inertia Constant of Synchronous Generator"
Post a Comment